Electric motors are one of the most important inventions of the modern era.
We use these marvels of engineering in almost every device we use today, from our cars to our vacuum cleaners.
Despite their ubiquitous nature, many of us still don’t fully understand how they work.
In this post, we will explore the mechanics of electric motors, how they operate, and the different types available.
We will delve into the principles of electromagnetism, how they relate to electric motors, and what makes them so efficient.
This article will help you understand the intricacies of electric motors and increase your appreciation for the marvels of contemporary engineering.
What Is Electric Motor: An Overview
Electric motors are an integral part of our modern world, powering a wide range of devices and machinery that we rely on daily.
From the moment we wake up to the time we go to bed, they work silently behind the scenes, propelling our lives forward.
At its core, an electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
It operates on the principle of electromagnetism, utilizing the interaction between electric current and magnetic fields to generate rotational motion.
This ingenious invention has revolutionized numerous industries, enhancing efficiency, productivity, and convenience.
The significance of electric motors in our everyday lives cannot be overstated.
They are the driving force behind household appliances such as washing machines, refrigerators, and air conditioners, making our domestic chores effortless.
In the automotive sector, they power hybrid and electric vehicles, paving the way for a more sustainable future.
Industries heavily rely on the robust performance of electric motors for manufacturing processes, transportation systems, and even robotics.
In addition to their versatility, electric motors offer numerous advantages.
They are highly efficient, converting a large percentage of electrical energy into useful mechanical work, reducing energy consumption and environmental impact.
It also provides precise control and smooth operation, ensuring optimal performance and user satisfaction.
As we delve deeper into the mechanics of electric motors, we will explore their fascinating components, principles of operation, and various types that exist.
The Basic Principles Behind Electric Motors
Electric motors are fascinating devices that have revolutionized the way we power various machines and appliances.
To truly appreciate their wonders, it is essential to understand the basic principles behind their operation.
At its core, an electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
This conversion is made possible through the interaction of magnetic fields and electric currents.
The motor consists of several essential components. These Include:
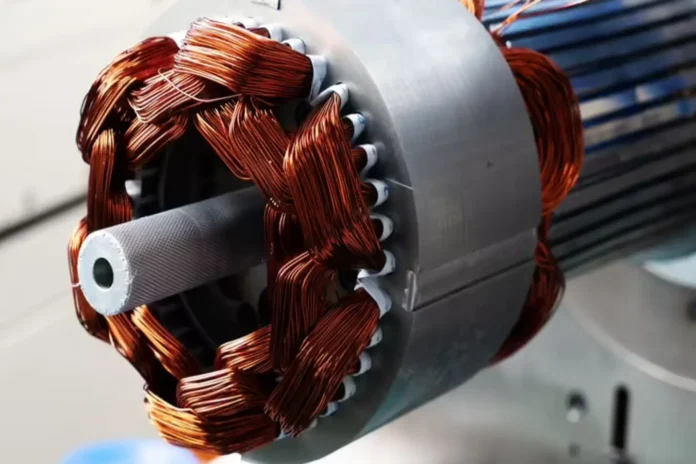
19The Stator
The stator is the stationary part of the motor and contains coils of wire, typically made from copper or aluminum.
These coils are wound around an iron core, creating electromagnetic fields when an electric current flows through them.
The stator serves as the source of the magnetic field that drives the motor’s operation.
18The Rotor
The rotor, on the other hand, is the rotating part of the motor.
It is usually made up of a cylindrical core with conductive bars or coils, also known as windings.
The rotor is designed to interact with the magnetic field generated by the stator.
When an electric current is applied to the windings, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with the stator’s field, resulting in rotational motion.
The power source provides the electrical energy needed to drive the motor.
This can be a direct current (DC) source or an alternating current (AC) source, depending on the type of motor.
DC motors rely on a steady flow of current in one direction, while AC motors can operate in the constantly changing direction of the current.
17The Commutator
The interaction between the magnetic fields produced by the stator and rotor creates a force that causes the rotor to rotate.
This rotational motion can then be harnessed to drive a wide range of applications, from powering industrial machinery to propelling electric vehicles.
Types Of Electric Motors
Electric motors are at the heart of countless devices and machines that we use in our daily lives.
From powering our cars to operating household appliances, electric motors play a crucial role in making our lives more convenient and efficient.
However, not all electric motors are created equal.
Understanding the different types is essential to truly grasp the intricate mechanics behind these remarkable inventions.
16Direct Current Motor
Firstly, we have the DC (direct current) motor, which is widely used in various applications.
As the name suggests, this type of motor operates on direct current, meaning the flow of electricity remains constant in one direction.
DC motors are known for their simplicity, reliability, and ease of control, making them ideal for devices like electric vehicles, robots, and small appliances.
15Alternative Current Motor
Next, we have the AC (alternating current) motor, which is the most commonly used type of electric motor.
AC motors work on alternating current, where the flow of electricity periodically changes direction.
This versatility allows AC motors to generate more power and operate at higher speeds.
Hence, they are suitable for a wide range of applications, including industrial machinery, HVAC systems, and pumps.
14Synchronous Motor
Another notable type is the synchronous motor, which is often employed in applications that require precise speed control.
Synchronous motors operate at a fixed speed, synchronized with the frequency of the power supply.
These motors are commonly found in clocks, timers, and industrial machinery where accurate timing is critical.
13Brushless DC Motors
Brushless DC motors, also known as BLDC motors, have gained popularity in recent years due to their higher efficiency and reliability.
Unlike traditional DC motors, BLDC motors use electronic commutation instead of brushes and commutators.
This design eliminates the need for maintenance and reduces the risk of wear and tear, making them ideal for power tools, electric vehicles, and computer cooling systems.
12Stepper Motors
Lastly, we have stepper motors, which are unique in their ability to move in precise increments or steps.
Stepper motors are widely used in applications that require precise positioning, such as 3D printers, CNC machines, and robotics.
By controlling the timing and sequence of electrical pulses, stepper motors can accurately control the rotation and movement of their output shafts.
Common Applications Of Electric Motors In Various Industries
Electric motors have become an integral part of numerous industries, revolutionizing the way we power and operate various machines and devices.
The versatility and efficiency of electric motors have made them indispensable in a wide range of applications across different sectors.
11Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, electric motors are commonly used in electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid vehicles, providing the power needed for propulsion.
The shift towards electric mobility has been driven by the environmental benefits and the increasing demand for sustainable transportation solutions.
They offer instantaneous torque and smooth acceleration, making them ideal for powering cars, buses, and even motorcycles.
10Manufacturing And Industrial Automation
Another industry where electric motors are widely utilized is manufacturing and industrial automation.
Electric motors play a crucial role in powering conveyor belts, robotic arms, and other machinery involved in production processes.
With their precise control and high efficiency, electric motors enable increased productivity, reduced energy consumption, and improved overall efficiency in manufacturing operations.
9The HVAC Industry
The HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) industry also heavily relies on electric motors for various applications.
Electric motors power fans, blowers, and compressors in HVAC systems, ensuring proper ventilation, temperature control, and air circulation in buildings and homes.
The use of electric motors in HVAC systems enhances energy efficiency and enables better control and customization of indoor environments.
8Renewable Energy Sector
Furthermore, electric motors find extensive applications in the renewable energy sector, particularly in wind turbines and solar power systems.
Wind turbines use electric motors to convert the kinetic energy of the wind into electrical energy.
Likewise, solar power systems employ electric motors to track the movement of the sun for optimal solar panel positioning.
Electric motors contribute to the sustainable generation of clean and renewable energy, supporting the global transition towards a greener future.
These are just a few examples of the common applications of electric motors in various industries.
Advantages Of Electric Motors
Electric motors have gained significant popularity in recent years due to their numerous advantages over traditional power sources.
7Electric Motors Are Highly Efficient
First and foremost, electric motors are highly efficient, converting a greater percentage of electrical energy into mechanical energy compared to internal combustion engines.
This energy efficiency leads to reduced energy consumption and lower operating costs, making electric motors a more sustainable and cost-effective choice.
6Electric Motors Are Environmentally friendly.
Another advantage of electric motors is their environmentally friendly nature.
Unlike internal combustion engines, electric motors produce zero tailpipe emissions, contributing to cleaner air quality and a reduced carbon footprint.
This makes them an ideal choice for industries and applications that prioritize sustainability and environmental stewardship.
5Electric Motors Also Offer Design Flexibility And Versatility
They can be easily integrated into various systems and applications, ranging from small household appliances to large-scale industrial machinery.
Additionally, electric motors provide precise and consistent speed control, enabling smooth and efficient operation in a wide range of operating conditions.
Limitations Of Electric Motors
However, it is important to acknowledge the limitations of electric motors as well.
4Depending On A Reliable Source Of Electricity
One limitation is the dependence on a reliable source of electricity. Without access to electricity, the functionality of electric motors is greatly hindered.
This can be a challenge in remote areas or during power outages.
3Higher Initial Investment
Additionally, electric motors typically require a higher initial investment compared to traditional power sources, which may deter some potential users.
2Limitations In Terms Of Power Density And Energy Storage
Furthermore, electric motors have certain limitations in terms of power density and energy storage.
While advancements in battery technology have improved energy storage capabilities, electric motors still face challenges in applications that require high power output. Or even extended operation without access to a power source.
Maintenance Tips To Prolong The Lifespan Of Electric Motors
Proper maintenance of electric motors is crucial to ensuring their longevity and optimal performance.
By following these tips and best practices, you can significantly prolong the lifespan of your electric motors.
Regular Inspections
First and foremost, regular inspections are essential.
Conduct visual inspections to check for any signs of wear, damage, or loose connections.
Look out for frayed wires, excessive heat, or unusual noises during operation.
If any issues are detected, address them promptly to prevent further damage.
Cleaning
Cleaning is another important aspect of maintenance.
Keep the motors clean and free from dust, dirt, and debris.
Regularly wipe down the motor housing and vents to prevent the accumulation of contaminants that can hinder proper cooling and ventilation.
Lubrication
Lubrication is key to maintaining smooth and efficient motor operation.
Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for lubrication intervals and use the recommended type of lubricant.
Ensure that the motor is properly lubricated to reduce friction and minimize wear on moving parts.
Pay Attention To The Motor’s Environment
Furthermore, pay attention to the motor’s environment.
Keep the motor protected from moisture, extreme temperatures, and corrosive substances.
Implement proper insulation and sealing to prevent water or dust ingress that can cause damage to the motor.
1Electrical Connections Should Be Inspected Regularly
You need to inspect all electrical connections regularly to ensure they are secure and free from corrosion.
Loose or faulty connections can lead to overheating and electrical malfunctions, which can shorten the lifespan of the motor.
Additionally, consider implementing surge protection devices to safeguard the motor against power fluctuations and voltage spikes.
Scheduling Regular Professional Maintenance
Lastly, consider scheduling regular professional maintenance or servicing for your electric motors.
Experienced technicians can provide thorough inspections, testing, and troubleshooting.
Hence, addressing any underlying issues that may not be apparent during routine maintenance
Frequently Asked Questions About Electric Motors
If you’re new to the world of electric motors, you may have some questions. Here are some frequently asked questions about electric motors:
An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It consists of a rotor (the moving part) and a stator (the stationary part) that work together to generate rotational motion.
Electric motors work on the principle of electromagnetism. When an electrical current passes through the coils of wire in the motor’s stator, it creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the permanent magnets on the rotor, causing it to rotate.
There are various types of electric motors, including AC (alternating current) motors, DC (direct current) motors, brushed and brushless motors, induction motors, and synchronous motors. Each type has its own unique characteristics and applications.
Electric motors offer several benefits over other types of motors. They are more energy-efficient, environmentally friendly, and require less maintenance. Electric motors also provide precise control and are capable of delivering high torque at low speeds.
Electric motors are used in a wide range of applications, from household appliances such as fans and refrigerators to industrial machinery, electric vehicles, and robotics. They are also used in HVAC systems, power tools, and many other devices that require mechanical motion.
My Final Thoughts on Electric Motors
In conclusion, electric motors are an essential component of modern society.
They are used in a wide range of applications, from powering household appliances to propelling electric vehicles.
Electric motors are efficient, reliable, and environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional combustion engines.
They work by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy, using magnetic fields and rotating components.
Advancements in technology have led to the development of more efficient and compact electric motors, making them even more valuable in various industries.
As we continue to prioritize sustainability and reduce our dependence on fossil fuels, electric motors will play a crucial role in shaping the future of transportation, manufacturing, and everyday life.
Whether it’s for powering our homes, operating machinery, or driving our vehicles, electric motors are here to stay.
I hope you find this guide helpful.
If you found the review helpful, kindly use the “Leave a Reply” form at the end of this page.
For more buying guides like this, please visit the following pages: